Erica L. Smith, BJS Statistician
December 2022
NCJ 305613
Female Murder Victims and Victim-Offender Relationship, 2021
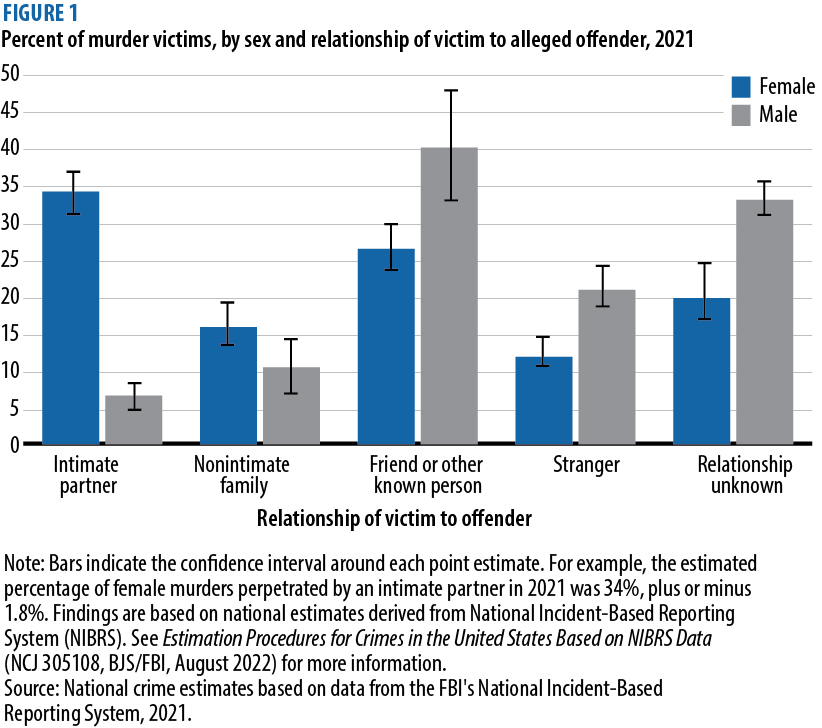
The percentage of females murdered by an intimate partner was 5 times higher than for males
Of the estimated 4,970 female victims of murder and nonnegligent manslaughter in 2021, data reported by law enforcement agencies indicate that 34% were killed by an intimate partner (figure 1). By comparison, about 6% of the 17,970 males murdered that year were victims of intimate partner homicide.
Overall, 76% of female murders and 56% of male murders were perpetrated by someone known to the victim. About 16% of female murder victims were killed by a nonintimate family member—parent, grandparent, sibling, in-law, and other family member—compared to 10% of male murder victims.
A larger percentage of males (21%) were murdered by a stranger than females (12%). For 1 out of every 3 male murder victims and 1 out of every 5 female murder victims, the relationship between the victim and the offender was unknown.
Methodology
About the data
The National Incident-Based Reporting System (NIBRS) is a data collection system designed and maintained by the FBI that compiles data on all crimes recorded by participating state and local law enforcement agencies. NIBRS captures extensive information on each incident known to law enforcement. The NIBRS database collects detailed information on 52 different offenses that can occur within a crime incident and collects arrest-only information for an additional 10 offenses.1 In 2021, national estimates of crime were based on data received from about 11,790 of the 18,800 law enforcement agencies in the United States, representing approximately 65% of the U.S. population. (See BJS’s National Incident-Based Reporting System page and the FBI’s Crime Data Explorer for more information.)
Definitions
Murder
Murder is composed of the two homicide categories: murder and nonnegligent manslaughter. The FBI defines murder and nonnegligent manslaughter as “The willful (nonnegligent) killing of one human being by another.”2 Attempted murders, accidental deaths, suicides, and traffic fatalities are not to be coded as murders in NIBRS. In addition, felony murder or situations where a victim dies of another cause (such as a heart attack) because of a crime being committed against them should not be classified as a murder.
Relationship of victim to alleged offender
The relationship of the victim to the alleged offender(s) is based on the NIBRS Relationship(s) of Victim to Offender(s) data element, which includes 27 distinct relationship types. For this analysis, the relationship types were aggregated into six categories, detailed below:
- Intimate partner—includes Victim Was Boyfriend/Girlfriend, Victim Was Common-Law Spouse, Victim Was Spouse, Victim Was Ex-Relationship (Ex-Boyfriend/Girlfriend), and Victim Was Ex-Spouse
- Nonintimate family—includes Victim Was Child, Victim Was Grandchild, Victim Was Grandparent, Victim Was In-law, Victim Was Other Family Member, Victim Was Parent, Victim Was Sibling, Victim Was Stepchild, Victim Was Stepparent, and Victim Was Stepsibling
- Friend or other known person—includes Victim Was Acquaintance, Victim Was Babysitter, Victim Was Child of Boyfriend or Girlfriend, Victim Was Employee, Victim Was Employer, Victim Was Friend, Victim Was Neighbor, and Victim Was Otherwise Known
- Stranger—includes Victim Was Stranger
- Victim was offender—includes Victim Was Offender; this relationship type is used to denote when a participant in a crime incident was both a victim and an offender, such as domestic disputes or bar fights where two or more persons were identified as participating
- Unknown relationship—includes Relationship Unknown
The relationship category Victim Was Offender is not included in this report. Less than 2% of murders and nonnegligent manslaughters in 2021 were estimated to include this type of relationship.
Calculating national estimates of crime based on NIBRS
Beginning with the 2021 data year, national estimates of crime known to law enforcement were based solely on NIBRS data. To calculate national estimates, BJS and the FBI partnered with RTI International to establish a new set of statistical procedures that would incorporate the NIBRS data structure and account for agencies that did not report data to the system. In October 2022, the FBI published the first set of national estimates derived from the new methodology; the data tables are available. For information about the development of the estimation procedures, including links to technical reports documenting the process, see the BJS NIBRS Estimation Project.
1Federal agencies submitting data to NIBRS may report an additional 19 offense types and 3 arrest-only offense types that are exclusive to federal crime incidents.
2NIBRS User Manual, page 29.